The vacuum blood collection device consists of three parts: vacuum blood collection tube, blood collection needle (including straight needle and scalp blood collection needle), and needle holder. Vacuum blood collection tube is the main component, mainly used for blood collection and storage. A certain amount of negative pressure is preset in the production process. When the blood collection needle punctures into the blood vessel, the blood automatically flows into the blood collection tube due to the negative pressure in the blood collection tube ; At the same time, various additives are preset in the blood collection tube, which can fully meet the clinical multiple comprehensive blood tests, safe, closed, and convenient for transportation.

Vacuum blood collection tubes and additives
Vacuum blood collection tubes are generally divided into the following types:
1. Dry empty tube without additives: The inner wall of the blood collection tube is evenly coated with the agent (silicone oil) to prevent wall hanging. It uses the principle of natural blood coagulation to coagulate the blood. After the serum is naturally precipitated, it is centrifuged for use. Mainly used for serum biochemistry (liver function, kidney function, myocardial enzymes, amylase, etc.), electrolytes (serum potassium, sodium, chloride, calcium, phosphorus, etc.), thyroid function, drug testing, AIDS testing, tumor markers, serum immunity learn.
2. Coagulation accelerator tube: the inner wall of the blood collection tube is evenly coated with silicone oil to prevent wall hanging, and coagulant is added. The coagulant can activate the fibrinase, so that the soluble fibrin becomes insoluble fibrin aggregates, and then forms a stable fibrin clot. If you want to get the result quickly, you can use the coagulation tube. Generally used in emergency biochemistry.
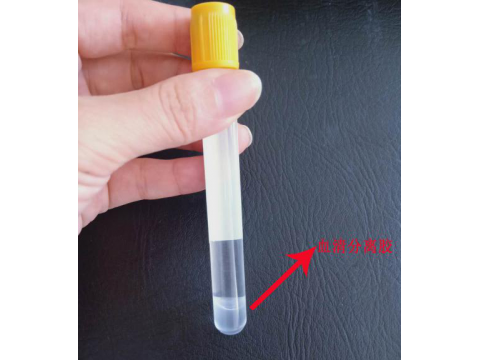
3. Blood collection tube containing separation gel and coagulant: The tube wall is siliconized and coated with coagulant to accelerate blood coagulation and shorten the inspection time. Separating glue is added in the tube. The separating glue has a good affinity with the PET tube, and it does play a role in isolation. Generally, even on ordinary centrifuges, the separating glue can remove the liquid components (serum) and solid components (blood cells) in the blood. Completely separate and accumulate in the test tube to form a barrier. After centrifugation, no oil droplets are produced in the serum, so the machine will not be blocked. Mainly used for serum biochemistry (liver function, kidney function, myocardial enzymes, amylase, etc.), electrolytes (serum potassium, sodium, chloride, calcium, phosphorus, etc.), thyroid function, drug testing, AIDS testing, tumor markers, serum immunity learn.
4. Blood collection tube containing anticoagulant in the tube:
1) Blood collection tubes containing heparin sodium or heparin lithium: Heparin is a mucopolysaccharide containing sulfuric acid groups with a strong negative charge, which can strengthen antithrombin III inactivation of serine proteases, thereby preventing thrombin Formed, and has a variety of anticoagulant effects such as preventing platelet aggregation. Heparin tubes are generally used for emergency biochemical and blood rheological testing. They are the best choice for electrolyte testing. When testing sodium ions in blood samples, heparin sodium should not be used to avoid affecting the test results. Nor can it be used for white blood cell counting and classification, because heparin can cause white blood cell aggregation.
2) Blood collection tubes containing ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and its salt (EDTA—): ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid is an amino polycarboxylic acid that can effectively chelate calcium ions in the blood. Chelating calcium will remove calcium from The removal of the reaction point will prevent and terminate the endogenous or exogenous coagulation process, thereby preventing blood clotting. Compared with other anticoagulants, it has less effect on the coagulation of blood cells and the morphology of blood cells, so EDTA salt is usually used (2K, 3K, 2Na) as anticoagulant. It is used for general hematology inspection, not for blood coagulation, trace element and PCR inspection.
3) Blood collection tubes containing sodium citrate anticoagulant: Sodium citrate acts as an anticoagulant by chelating calcium ions in the blood sample. The National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standardization (NCCLS) recommends 3.2% or 3.8%, anticoagulant The ratio of agent to blood is 1:9, which is mainly used in the fibrinolytic system (prothrombin time, thrombin time, activated partial thrombin time, fibrinogen). Attention should be paid to sufficient blood volume during blood collection to ensure the accuracy of the test results. After blood collection, it should be inverted and mixed 5-8 times immediately.
4) The tube contains potassium oxalate/sodium fluoride (1 part of sodium fluoride and 3 parts of potassium oxalate): Sodium fluoride is a weak anticoagulant, which has a good effect on preventing blood sugar degradation and is an excellent preservative for blood sugar testing. When using, pay attention to slowly inverting and mixing. It is generally used for blood glucose testing, not for the urease method to determine urea, nor for alkaline phosphatase and amylase.